This C++ version of BAT is still being maintained, but addition of new features is unlikely. Check out our new incarnation, BAT.jl, the Bayesian analysis toolkit in Julia. In addition to Metropolis-Hastings sampling, BAT.jl supports Hamiltonian Monte Carlo (HMC) with automatic differentiation, automatic prior-based parameter space transformations, and much more. See the BAT.jl documentation.
Results of performance testing for BAT version 0.9
Back to | overview for 0.9 | all versions |
Test "1d_poisson_20"
| Results | |
|---|---|
| Status | good |
| CPU time | 21.94 s |
| Real time | 22.19 s |
| Plots | 1d_poisson_20.ps |
| Log | 1d_poisson_20.log |
| Settings | |
|---|---|
| N chains | 10 |
| N lag | 10 |
| Convergence | true |
| N iterations (pre-run) | 1000 |
| N iterations (run) | 10000000 |
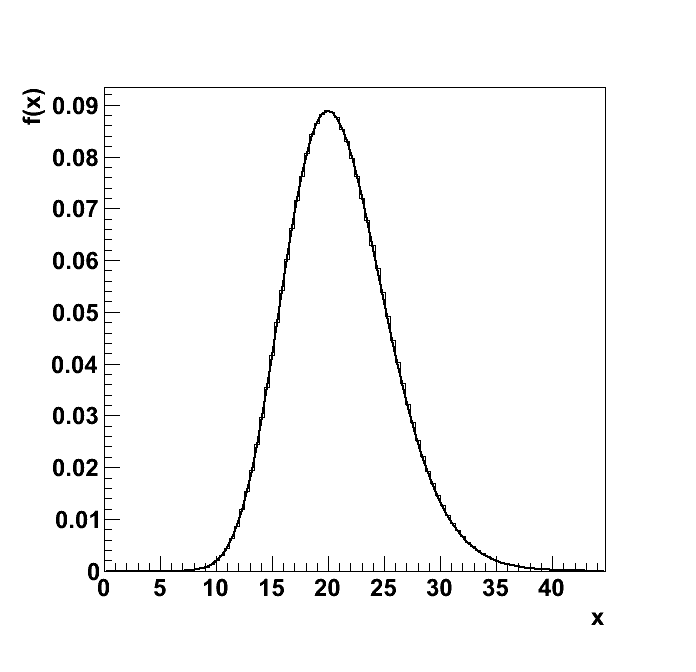
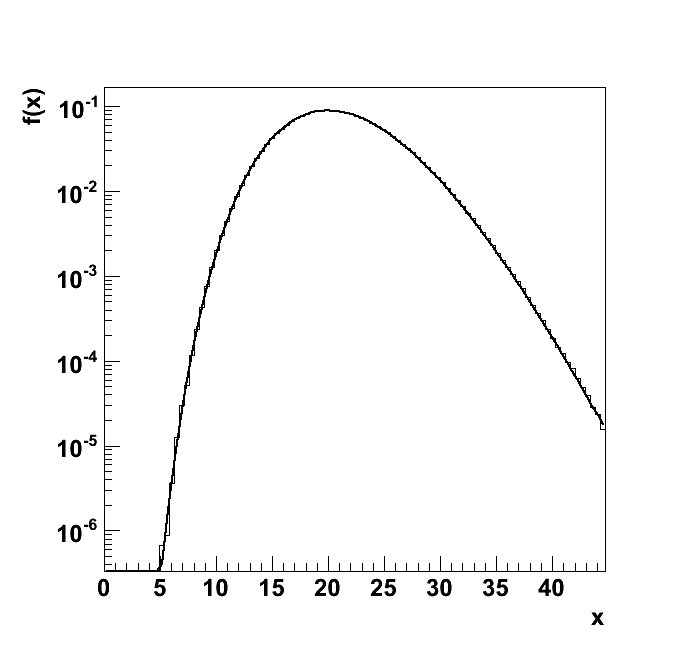
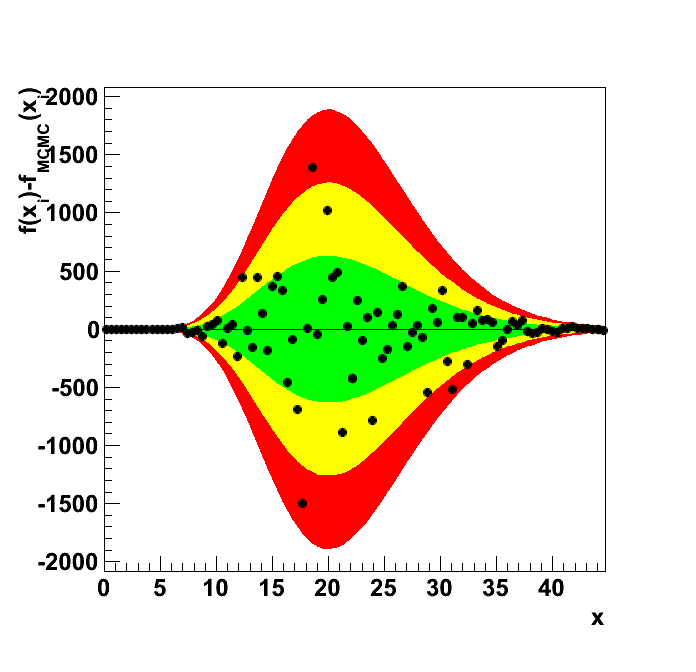
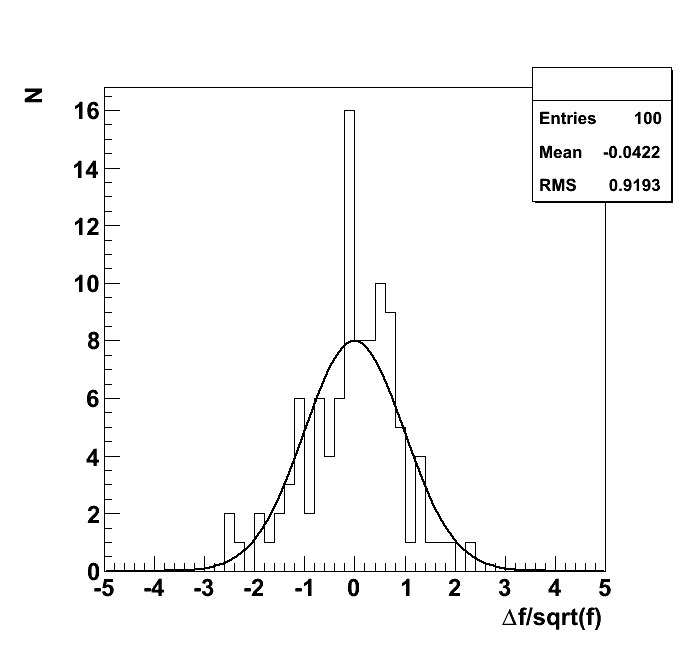
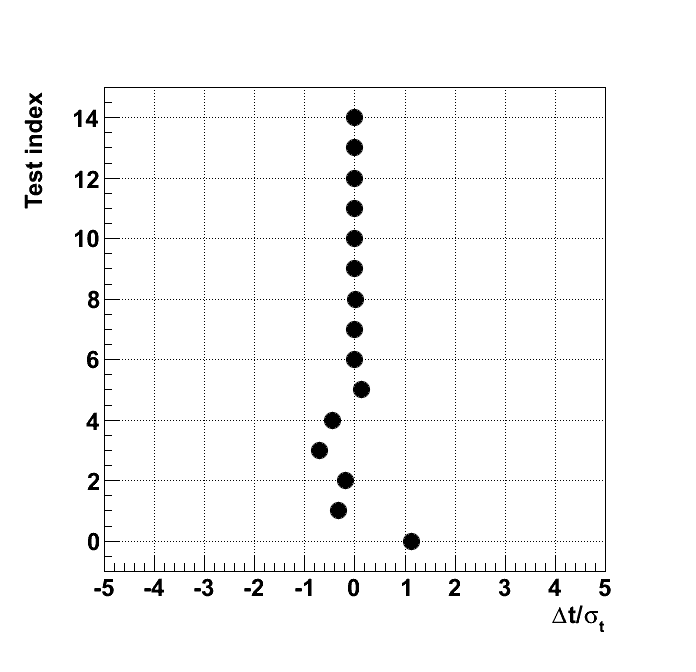
Plots
| Subtest | Status | Target | Test | Uncertainty | Deviation [%] | Deviation [sigma] | Tol. (Good) | Tol. (Acceptable) | Tol. (Bad) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
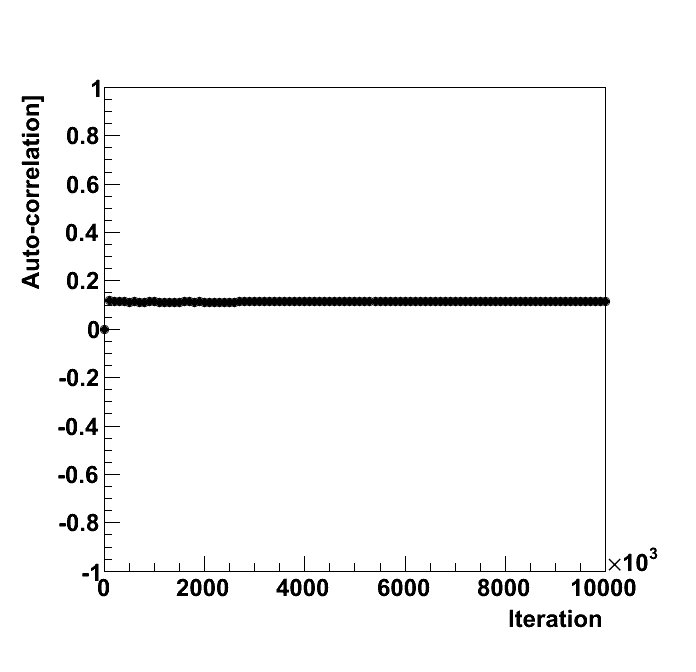
| correlation par 0 | off | 0 | 0.1136 | 0.01125 | - | -10.1 | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.7 |
| chi2 | good | 87 | 82.55 | 13.19 | -5.114 | 0.3373 | 39.57 | 65.95 | 92.34 |
| KS | good | 1 | 0.9431 | 0.95 | -5.689 | 0.05989 | 0.95 | 0.99 | 0.9999 |
| mean | good | 21 | 21 | 0.00145 | -0.004913 | 0.7117 | 0.00435 | 0.007249 | 0.01015 |
| mode | good | 20 | 19.9 | 0.2229 | -0.495 | 0.4441 | 0.6687 | 1.115 | 1.56 |
| variance | good | 20.98 | 21.41 | 3.171 | 2.02 | -0.1336 | 9.514 | 15.86 | 22.2 |
| quantile10 | good | 15.38 | 15.37 | 0.2229 | -0.01247 | 0.008602 | 0.6687 | 1.115 | 1.56 |
| quantile20 | good | 17.08 | 17.07 | 0.2229 | -0.007027 | 0.005383 | 0.6687 | 1.115 | 1.56 |
| quantile30 | good | 18.38 | 18.38 | 0.2229 | 0.006908 | -0.005695 | 0.6687 | 1.115 | 1.56 |
| quantile40 | good | 19.54 | 19.54 | 0.2229 | -0.001885 | 0.001652 | 0.6687 | 1.115 | 1.56 |
| quantile50 | good | 20.67 | 20.67 | 0.2229 | -0.01093 | 0.01013 | 0.6687 | 1.115 | 1.56 |
| quantile60 | good | 21.84 | 21.84 | 0.2229 | -0.008247 | 0.00808 | 0.6687 | 1.115 | 1.56 |
| quantile70 | good | 23.14 | 23.14 | 0.2229 | -0.007524 | 0.007812 | 0.6687 | 1.115 | 1.56 |
| quantile80 | good | 24.73 | 24.73 | 0.2229 | -0.004678 | 0.00519 | 0.6687 | 1.115 | 1.56 |
| quantile90 | good | 27.05 | 27.05 | 0.2229 | -0.008308 | 0.01008 | 0.6687 | 1.115 | 1.56 |
| Subtest | Description |
|---|---|
| correlation par 0 | Calculate the auto-correlation among the points. |
| chi2 | Calculate χ2 and compare with prediction for dof=number of bins with an expectation >= 10. Tolerance good: |χ2-E[χ2]| < 3 · (2 dof)1/2, Tolerance acceptable: |χ2-E[χ2]| < 5 · (2 dof)1/2, Tolerance bad: |χ2-E[χ2]| < 7 · (2 dof)1/2. |
| KS | Calculate the Kolmogorov-Smirnov probability based on the ROOT implemention. Tolerance good: KS prob > 0.05, Tolerance acceptable: KS prob > 0.01 Tolerance bad: KS prob > 0.0001. |
| mean | Compare sample mean, <x>, with expectation value of function, E[x]. Tolerance good: |<x> -E[x]| < 3 · (V[x]/n)1/2, Tolerance acceptable: |<x> -E[x]| < 5 · (V[x]/n)1/2, Tolerance bad: |<x> -E[x]| < 7 · (V[x]/n)1/2. |
| mode | Compare mode of distribution with mode of the analytic function. Tolerance good: |x*-mode| < 3 · V[mode]1/2, Tolerance acceptable: |x*-mode| < 5 · V[mode]1/2 bin widths, Tolerance bad: |x*-mode| < 7 · V[mode]1/2. |
| variance | Compare sample variance s2 of distribution with variance of function. Tolerance good: 3 · V[s2]1/2, Tolerance acceptable: 5 · V[s2]1/2, Tolerance bad: 7 · V[s2]1/2. |
| quantile10 | Compare quantile of distribution from MCMC with the quantile of analytic function. Tolerance good: |q_{X}-E[q_{X}]|<3·V[q]1/2, Tolerance acceptable: |q_{X}-E[q_{X}]|<5·V[q]1/2, Tolerance bad: |q_{X}-E[q_{X}]|<7·V[q]1/2. |
| quantile20 | Compare quantile of distribution from MCMC with the quantile of analytic function. Tolerance good: |q_{X}-E[q_{X}]|<3·V[q]1/2, Tolerance acceptable: |q_{X}-E[q_{X}]|<5·V[q]1/2, Tolerance bad: |q_{X}-E[q_{X}]|<7·V[q]1/2. |
| quantile30 | Compare quantile of distribution from MCMC with the quantile of analytic function. Tolerance good: |q_{X}-E[q_{X}]|<3·V[q]1/2, Tolerance acceptable: |q_{X}-E[q_{X}]|<5·V[q]1/2, Tolerance bad: |q_{X}-E[q_{X}]|<7·V[q]1/2. |
| quantile40 | Compare quantile of distribution from MCMC with the quantile of analytic function. Tolerance good: |q_{X}-E[q_{X}]|<3·V[q]1/2, Tolerance acceptable: |q_{X}-E[q_{X}]|<5·V[q]1/2, Tolerance bad: |q_{X}-E[q_{X}]|<7·V[q]1/2. |
| quantile50 | Compare quantile of distribution from MCMC with the quantile of analytic function. Tolerance good: |q_{X}-E[q_{X}]|<3·V[q]1/2, Tolerance acceptable: |q_{X}-E[q_{X}]|<5·V[q]1/2, Tolerance bad: |q_{X}-E[q_{X}]|<7·V[q]1/2. |
| quantile60 | Compare quantile of distribution from MCMC with the quantile of analytic function. Tolerance good: |q_{X}-E[q_{X}]|<3·V[q]1/2, Tolerance acceptable: |q_{X}-E[q_{X}]|<5·V[q]1/2, Tolerance bad: |q_{X}-E[q_{X}]|<7·V[q]1/2. |
| quantile70 | Compare quantile of distribution from MCMC with the quantile of analytic function. Tolerance good: |q_{X}-E[q_{X}]|<3·V[q]1/2, Tolerance acceptable: |q_{X}-E[q_{X}]|<5·V[q]1/2, Tolerance bad: |q_{X}-E[q_{X}]|<7·V[q]1/2. |
| quantile80 | Compare quantile of distribution from MCMC with the quantile of analytic function. Tolerance good: |q_{X}-E[q_{X}]|<3·V[q]1/2, Tolerance acceptable: |q_{X}-E[q_{X}]|<5·V[q]1/2, Tolerance bad: |q_{X}-E[q_{X}]|<7·V[q]1/2. |
| quantile90 | Compare quantile of distribution from MCMC with the quantile of analytic function. Tolerance good: |q_{X}-E[q_{X}]|<3·V[q]1/2, Tolerance acceptable: |q_{X}-E[q_{X}]|<5·V[q]1/2, Tolerance bad: |q_{X}-E[q_{X}]|<7·V[q]1/2. |