This C++ version of BAT is still being maintained, but addition of new features is unlikely. Check out our new incarnation, BAT.jl, the Bayesian analysis toolkit in Julia. In addition to Metropolis-Hastings sampling, BAT.jl supports Hamiltonian Monte Carlo (HMC) with automatic differentiation, automatic prior-based parameter space transformations, and much more. See the BAT.jl documentation.
Results of performance testing for BAT version 0.9
Back to | overview for 0.9 | all versions |
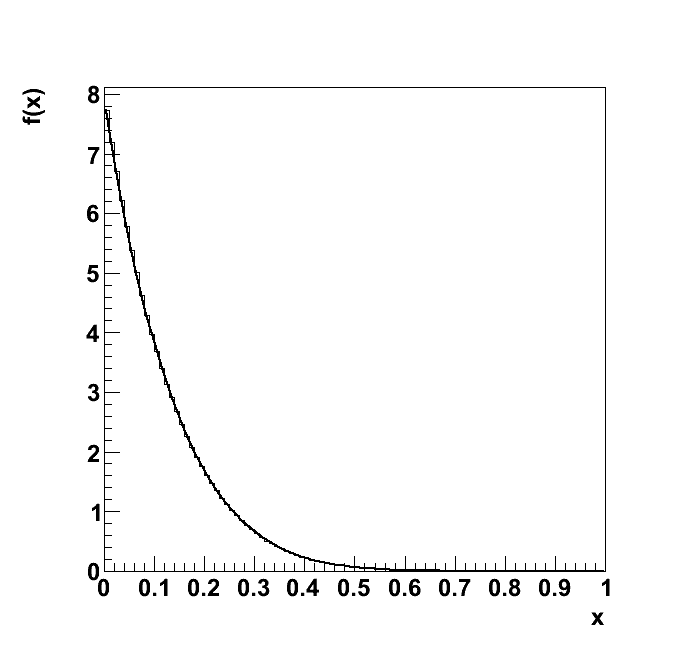
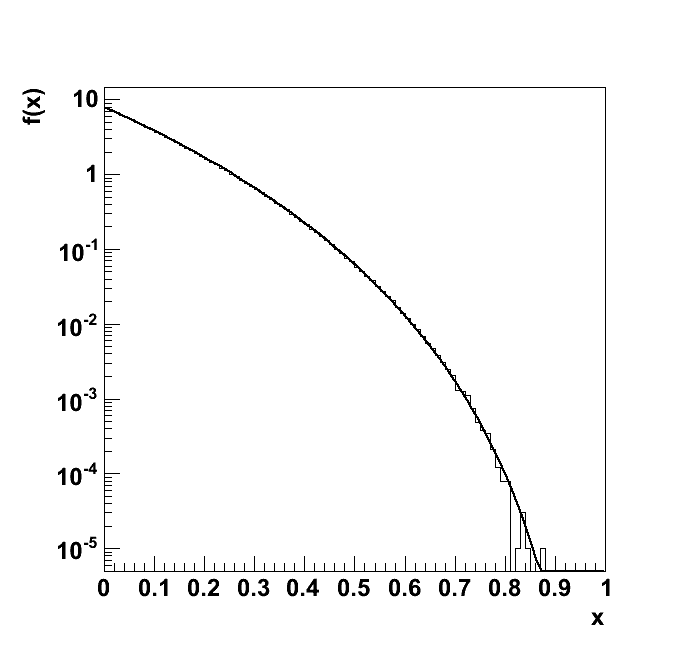
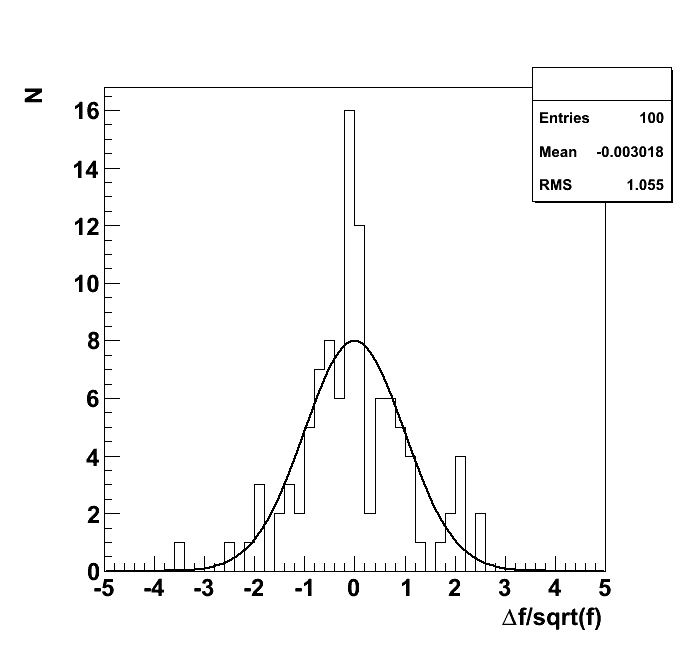
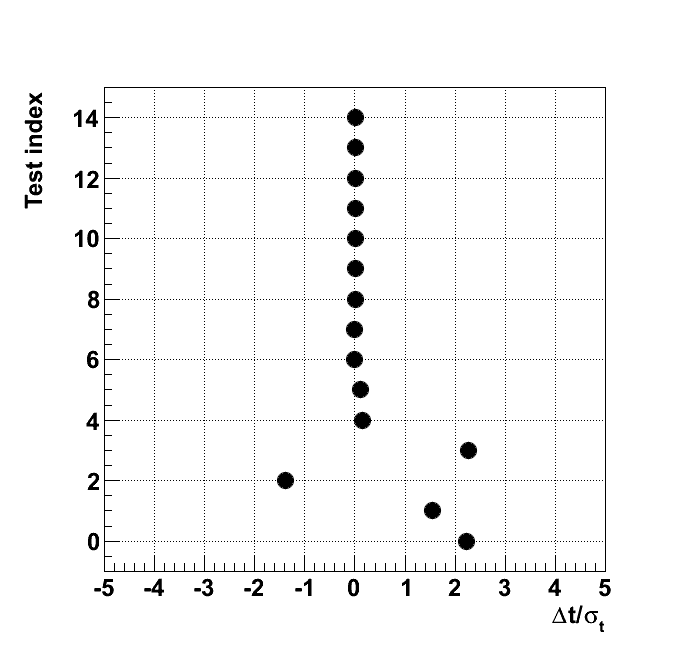
Test "1d_binomial_0_7"
| Results | |
|---|---|
| Status | good |
| CPU time | 147.7 s |
| Real time | 148 s |
| Plots | 1d_binomial_0_7.ps |
| Log | 1d_binomial_0_7.log |
| Settings | |
|---|---|
| N chains | 10 |
| N lag | 10 |
| Convergence | true |
| N iterations (pre-run) | 2000 |
| N iterations (run) | 10000000 |
| Subtest | Status | Target | Test | Uncertainty | Deviation [%] | Deviation [sigma] | Tol. (Good) | Tol. (Acceptable) | Tol. (Bad) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
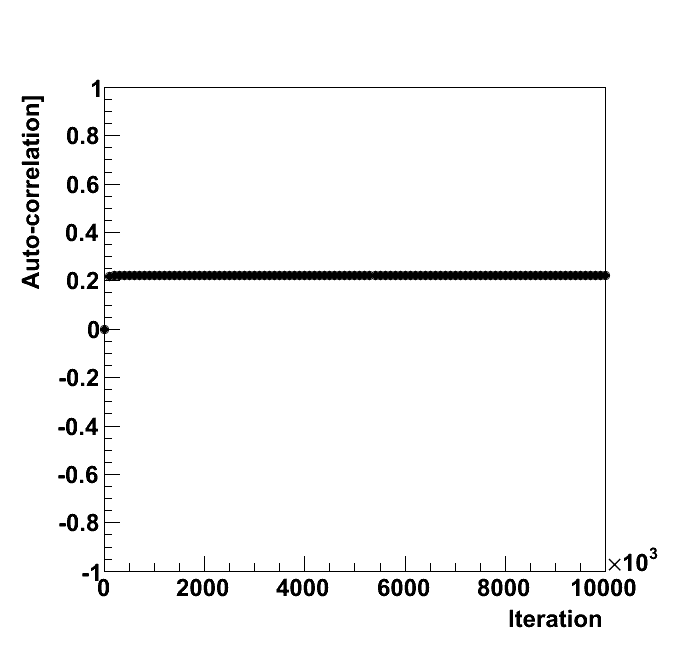
| correlation par 0 | off | 0 | 0.222 | 0.02193 | - | -10.12 | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.7 |
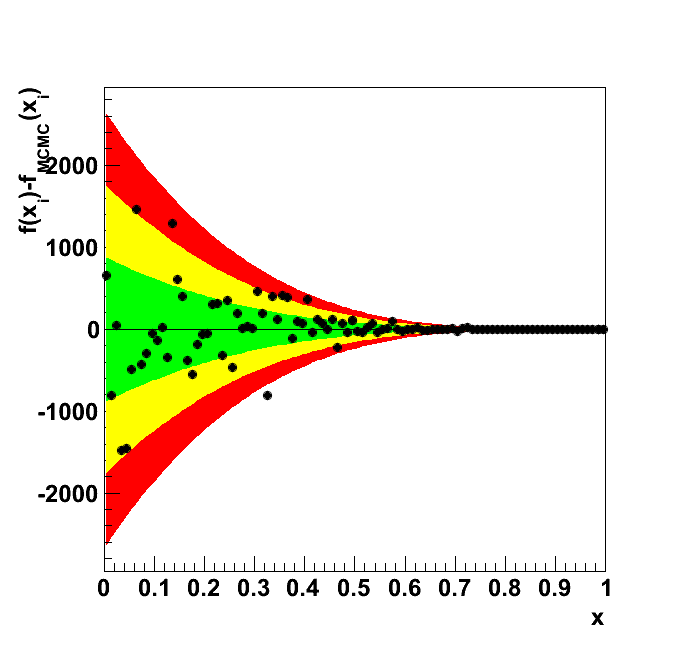
| chi2 | good | 80 | 99.58 | 12.65 | 24.47 | -1.548 | 37.95 | 63.25 | 88.54 |
| KS | good | 1 | 0.5592 | 0.95 | -44.08 | 0.464 | 0.95 | 0.99 | 0.9999 |
| mean | good | 0.1111 | 0.1112 | 3.147e-05 | 0.06403 | -2.261 | 9.44e-05 | 0.0001573 | 0.0002203 |
| mode | good | 0 | 0.005 | 0.03333 | - | -0.15 | 0.1 | 0.1667 | 0.2333 |
| variance | good | 0.009877 | 0.01009 | 0.002049 | 2.144 | -0.1033 | 0.006147 | 0.01025 | 0.01434 |
| quantile10 | good | 0.01316 | 0.01315 | 0.03333 | -0.0425 | 0.0001678 | 0.1 | 0.1667 | 0.2333 |
| quantile20 | good | 0.02757 | 0.02758 | 0.03333 | 0.00642 | -5.311e-05 | 0.1 | 0.1667 | 0.2333 |
| quantile30 | good | 0.04369 | 0.04373 | 0.03333 | 0.08408 | -0.001102 | 0.1 | 0.1667 | 0.2333 |
| quantile40 | good | 0.06191 | 0.06198 | 0.03333 | 0.105 | -0.001949 | 0.1 | 0.1667 | 0.2333 |
| quantile50 | good | 0.08308 | 0.08314 | 0.03333 | 0.07304 | -0.00182 | 0.1 | 0.1667 | 0.2333 |
| quantile60 | good | 0.1083 | 0.1084 | 0.03333 | 0.07463 | -0.002424 | 0.1 | 0.1667 | 0.2333 |
| quantile70 | good | 0.1397 | 0.1398 | 0.03333 | 0.05066 | -0.002124 | 0.1 | 0.1667 | 0.2333 |
| quantile80 | good | 0.1823 | 0.1824 | 0.03333 | 0.05727 | -0.003132 | 0.1 | 0.1667 | 0.2333 |
| quantile90 | good | 0.2501 | 0.2503 | 0.03333 | 0.06285 | -0.004716 | 0.1 | 0.1667 | 0.2333 |
| Subtest | Description |
|---|---|
| correlation par 0 | Calculate the auto-correlation among the points. |
| chi2 | Calculate χ2 and compare with prediction for dof=number of bins with an expectation >= 10. Tolerance good: |χ2-E[χ2]| < 3 · (2 dof)1/2, Tolerance acceptable: |χ2-E[χ2]| < 5 · (2 dof)1/2, Tolerance bad: |χ2-E[χ2]| < 7 · (2 dof)1/2. |
| KS | Calculate the Kolmogorov-Smirnov probability based on the ROOT implemention. Tolerance good: KS prob > 0.05, Tolerance acceptable: KS prob > 0.01 Tolerance bad: KS prob > 0.0001. |
| mean | Compare sample mean, <x>, with expectation value of function, E[x]. Tolerance good: |<x> -E[x]| < 3 · (V[x]/n)1/2,Tolerance acceptable: |<x> -E[x]| < 5 · (V[x]/n)1/2,Tolerance bad: |<x> -E[x]| < 7 · (V[x]/n)1/2. |
| mode | Compare mode of distribution with mode of the analytic function. Tolerance good: |x*-mode| < 3 · V[mode]1/2, Tolerance acceptable: |x*-mode| < 5 · V[mode]1/2 bin widths, Tolerance bad: |x*-mode| < 7 · V[mode]1/2. |
| variance | Compare sample variance s2 of distribution with variance of function. Tolerance good: 3 · V[s2]1/2, Tolerance acceptable: 5 · V[s2]1/2, Tolerance bad: 7 · V[s2]1/2. |
| quantile10 | Compare quantile of distribution from MCMC with the quantile of analytic function. Tolerance good: |q_{X}-E[q_{X}]|<3·V[q]1/2, Tolerance acceptable: |q_{X}-E[q_{X}]|<5·V[q]1/2, Tolerance bad: |q_{X}-E[q_{X}]|<7·V[q]1/2. |
| quantile20 | Compare quantile of distribution from MCMC with the quantile of analytic function. Tolerance good: |q_{X}-E[q_{X}]|<3·V[q]1/2, Tolerance acceptable: |q_{X}-E[q_{X}]|<5·V[q]1/2, Tolerance bad: |q_{X}-E[q_{X}]|<7·V[q]1/2. |
| quantile30 | Compare quantile of distribution from MCMC with the quantile of analytic function. Tolerance good: |q_{X}-E[q_{X}]|<3·V[q]1/2, Tolerance acceptable: |q_{X}-E[q_{X}]|<5·V[q]1/2, Tolerance bad: |q_{X}-E[q_{X}]|<7·V[q]1/2. |
| quantile40 | Compare quantile of distribution from MCMC with the quantile of analytic function. Tolerance good: |q_{X}-E[q_{X}]|<3·V[q]1/2, Tolerance acceptable: |q_{X}-E[q_{X}]|<5·V[q]1/2, Tolerance bad: |q_{X}-E[q_{X}]|<7·V[q]1/2. |
| quantile50 | Compare quantile of distribution from MCMC with the quantile of analytic function. Tolerance good: |q_{X}-E[q_{X}]|<3·V[q]1/2, Tolerance acceptable: |q_{X}-E[q_{X}]|<5·V[q]1/2, Tolerance bad: |q_{X}-E[q_{X}]|<7·V[q]1/2. |
| quantile60 | Compare quantile of distribution from MCMC with the quantile of analytic function. Tolerance good: |q_{X}-E[q_{X}]|<3·V[q]1/2, Tolerance acceptable: |q_{X}-E[q_{X}]|<5·V[q]1/2, Tolerance bad: |q_{X}-E[q_{X}]|<7·V[q]1/2. |
| quantile70 | Compare quantile of distribution from MCMC with the quantile of analytic function. Tolerance good: |q_{X}-E[q_{X}]|<3·V[q]1/2, Tolerance acceptable: |q_{X}-E[q_{X}]|<5·V[q]1/2, Tolerance bad: |q_{X}-E[q_{X}]|<7·V[q]1/2. |
| quantile80 | Compare quantile of distribution from MCMC with the quantile of analytic function. Tolerance good: |q_{X}-E[q_{X}]|<3·V[q]1/2, Tolerance acceptable: |q_{X}-E[q_{X}]|<5·V[q]1/2, Tolerance bad: |q_{X}-E[q_{X}]|<7·V[q]1/2. |
| quantile90 | Compare quantile of distribution from MCMC with the quantile of analytic function. Tolerance good: |q_{X}-E[q_{X}]|<3·V[q]1/2, Tolerance acceptable: |q_{X}-E[q_{X}]|<5·V[q]1/2, Tolerance bad: |q_{X}-E[q_{X}]|<7·V[q]1/2. |